id生成
分布式场景下全局唯一id的生成方案,雪花算法、数据库自增、redis自增。
1. 雪花算法
1.1 结构
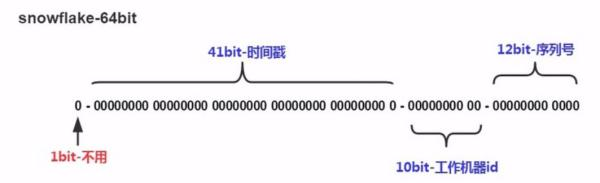
- 41bit时间戳:这里采用的就是当前系统的具体时间,单位为毫秒
- 10bit工作机器ID(workerId):每台机器分配一个id,这样可以标示不同的机器,但是上限为1024,标示一个集群某个业务最多部署的机器个数上限
- 12bit序列号(自增域):表示在某一毫秒下,这个自增域最大可以分配的bit个数,在当前这种配置下,每一毫秒可以分配2^12个数据,也就是说QPS可以到 409.6 w/s。
1.2 代码实现
可以用hutool中的工具类IdUtil来创建雪花算法生成的id
导入
hutool1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.7.2</version>
</dependency>使用
IdUtil1
2
3
4
5IdUtil.createSnowflake(0L,1L);
//传入参数是workerId和datacenterId
public static Snowflake createSnowflake(long workerId, long datacenterId) {
return new Snowflake(workerId, datacenterId);
}
代码剖析:
初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47//上方函数调用的构造参数,进行初始化
public Snowflake(long workerId, long dataCenterId) {
this(workerId, dataCenterId, false);
}
public Snowflake(long workerId, long dataCenterId, boolean isUseSystemClock) {
this((Date)null, workerId, dataCenterId, isUseSystemClock);
}
public Snowflake(Date epochDate, long workerId, long dataCenterId, boolean isUseSystemClock) {
this.workerIdBits = 5L;
//最大workerId,5位也就是2^5-1
this.maxWorkerId = 31L;
this.dataCenterIdBits = 5L;
//最大dataCenterId,5位也就是2^5-1
this.maxDataCenterId = 31L;
this.sequenceBits = 12L;
this.workerIdShift = 12L;
this.dataCenterIdShift = 17L;
this.timestampLeftShift = 22L;
//最大序列号,2^12 - 1
this.sequenceMask = 4095L;
this.sequence = 0L;
this.lastTimestamp = -1L;
//使用工具类传的是null
if (null != epochDate) {
this.twepoch = epochDate.getTime();
} else {
this.twepoch = 1288834974657L;
}
if (workerId <= 31L && workerId >= 0L) {
if (dataCenterId <= 31L && dataCenterId >= 0L) {
this.workerId = workerId;
this.dataCenterId = dataCenterId;
this.useSystemClock = isUseSystemClock;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(StrUtil.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than {} or less than 0", new Object[]{31L}));
}
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(StrUtil.format("worker Id can't be greater than {} or less than 0", new Object[]{31L}));
}
}具体创建逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27public synchronized long nextId() {
//生成的时间戳13位,默认的twepoch也是13位
long timestamp = this.genTime();
//时间片回拨问题,时间差较小进行同步,时间差较大直接抛异常
if (timestamp < this.lastTimestamp) {
if (this.lastTimestamp - timestamp >= 2000L) {
throw new IllegalStateException(StrUtil.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for {}ms", new Object[]{this.lastTimestamp - timestamp}));
}
timestamp = this.lastTimestamp;
}
//序号自增,增到最大再次将时间戳更新(防止id重复)
if (timestamp == this.lastTimestamp) {
long sequence = this.sequence + 1L & 4095L;
if (sequence == 0L) {
timestamp = this.tilNextMillis(this.lastTimestamp);
}
this.sequence = sequence;
} else {
this.sequence = 0L;
}
this.lastTimestamp = timestamp;
//创建Id,(时间戳 - 1288834974657L) + 五位的dtaCenterId + 五位的workerId + 12位序列号
//很符合雪花算法的结构 时间戳 + 10位机器Id + 12位序列号
return timestamp - this.twepoch << 22 | this.dataCenterId << 17 | this.workerId << 12 | this.sequence;
}
1.3 问题
雪花算法可能出现以下问题
- 时间片回拨:由于机器的时间是动态的调整的,有可能会出现时间跑到之前几毫秒,如果这个时候获取到了这种时间,则会出现id重复
- 机器id分配以及回收:机器id需要每台机器不一样,这样的方式分配需要有方案进行处理,同时也要考虑,如果该机器宕机了,对应的workerId分配后的回收问题
- 机器id上线:机器id是固定的bit,那么也就是对应的机器个数是有上限的,在有些业务场景下,需要所有机器共享同一个业务空间,那么10bit表示的1024台机器是不够的。
解决方案
问题的处理没有完美的方案,只要选一个适合自身业务场景的就行
时间回拨问题
- 出现回拨直接抛异常
- 采用等待跟上次时间的一段范围:这种算是简单解决,可以接受,但是如果等待一段时间后再出现回拨,则抛异常。(hutool工具包中就采用的这种方案)
机器id上限
这个问题受限于雪花算法的结构,除非改一下雪花算法增加机器Id位数,不然没法解决
机器id分配问题
机器id分配问题比起雪花算法,它和业务的关联性更大,这里单独拿出来说一下。
在上面代码中,我们使用hutool工具包随便传入了两个值作为workerId和datacenterId,但真实生产环境中这两个值是需要有一套分配策略来产生的(多个不同的Java程序使用相同的机器id可能会导致id重复生成)。
需求:
- 机器id需要能够不重复的分配给所有JVM实例
- 机器id数量有限,需要对不使用的机器id进行回收复用
1.3.1 直接使用ip地址
服务器的IP地址一般都是公司的内网IP,子网划分时同一子网IP的前几位基本是相同的,根据这一特性我们可以在IP地址中取10位作为机器id。
1 | public class IDGenerator { |
一台机器多个JVM或者ip地址最后十位相同时会导致机器id重复
1.3.2 redis维护机器id
参考失败的面的文章
redis不保证可用性,可能会导致机器id重复
1.3.3 zookeeper维护机器id
通过创建分区来监控服务器的状态
2. 数据库自增
在数据库中创建一张表来维护全局唯一的自增id
建表
数据库表中id可能供多个服务使用,加上
type区分使用场景( 用户表需要自增id,其它表可能也需要),代码实现中可以定义枚举类来记录type1
2
3
4
5
6
7CREATE TABLE `serial_number` (
`number` bigint DEFAULT '0',
`type` varchar(255) NOT NULL COMMENT '自增id类型',
`create_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3),
`update_time` datetime(3) NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3) ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(3),
PRIMARY KEY (`type`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 commit '全局自增id表'编写代码
数据库操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
<mapper namespace="org.example.learn.mapper.SerialNumberMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="org.example.learn.entity.SerialNumber">
<id property="type" column="type" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="number" column="number" jdbcType="BIGINT"/>
<result property="createTime" column="create_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"/>
<result property="updateTime" column="update_time" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getId" resultType="java.lang.Long">
select number
from serial_number
where type = #{type} FOR UPDATE;
</select>
<insert id="insert" >
insert into serial_number
( type,number)
values (#{type},#{number});
</insert>
<update id="increment" >
update serial_number
set number = number + 1
where type = #{type};
</update>
</mapper>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13package org.example.learn.mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
public interface SerialNumberMapper {
int insert(Long number,String type);
Long getId( Long id);
int increment(String type);
}id生成服务
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21//id生成的具体逻辑
//加事务保证外层事务回滚时,id生成也跟着回滚
public class SerialNumberServiceImpl implements SerialNumberService {
private SerialNumberMapper serialNumberMapper;
public Long getId(){
Long num = serialNumberMapper.getId("test");
if(num == null||num == 0){
serialNumberMapper.insert(1L,"test");
return 1L;
}else{
if(serialNumberMapper.increment("test")==1){
return num+1;
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("data error");
}
}
}
}
3. redis生成ID
可以用redis定义一个Hash类型或者多个key来表示要用的Id,每次使用的时候incr自增就行了。
Redisson 中有AtmoicLong类型数据可以用作自增id,引用自 修己xj
1 |
|
问题:不过redis作为内存数据库,不保证可用性,它的数据不是一定能保证正确存储的。所以id可能会出现重复,这时需要进行一定的处理,比如抛异常,更新redis值等。
4. 其他
ID的生成不拘泥于形式只要能满足业务的需求就行,除了这些常见的id生成策略还可以
UUID生成随机字符串
自行拼接日期、随机数、业务中值等内容形成ID
…